- Home
- Products and Software
- What Is Website Hosting? A Beginner’s Guide
As a tech business owner or tech freelancer running one or multiple eCommerce businesses, one term you will hear often is ‘website hosting’. It really doesn’t matter the type of eCommerce business you own or if you manage a Software as a Service (SaaS) corporation, website hosting is a critical component of your online presence.
Think of your website as your digital storefront, where customers from all over the world can visit, browse, and purchase your digital products or services. Just as a physical store needs a physical location, your online store or SaaS platform requires a virtual space to exist – that’s where website hosting comes into play.
Website hosting serves as the foundation for your online presence, providing the infrastructure necessary to make your website accessible to anyone with an internet connection. It’s like leasing a piece of land in the digital realm where you can build and customize your online space to suit your brand and cater to your audience.
So, what is website hosting? In this blog, we’ll answer all your questions about website hosting, and help you understand why it is important to the success of your online business.
Let’s get started!
What is Website Hosting?
Website Hosting, or Web hosting, refers to the process of storing and serving website files, data, and content on specialized servers connected to the internet. These servers are maintained and operated by website hosting companies, data centers, or cloud service providers.
When you create a website, it consists of various files, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, videos, and databases. Web hosting makes these files accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
In simpler terms, website hosting is like renting a home for your website on the internet. Imagine your website as a house, and web hosting is the land and infrastructure where your house stands.
How Does Website Hosting Work?
Here’s how it works:
- The Internet: Think of the internet as a vast city. Your website is like a house in that city. To make your house accessible to people, you need a specific location (website hosting) for it.
- Web Host: A website hosting company is like a real estate agency. They have big, powerful computers called servers. These servers store all the files, images, and content that make up your website.
- Domain Name: Just like houses have addresses, your website needs an address too. This address is called a domain name (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com). The domain name is like your street address in the city, directing people to your website.
- Visitor Requests: When someone wants to visit your website, they type your domain name into their web browser. The browser then sends a request to your hosting company’s server, asking for your website’s files.
- Server Response: The hosting server receives the request and sends back the necessary files to the visitor’s browser. This allows the visitor to see your website on their screen.
- 24/7 Access: Your hosting company ensures that your website is available 24/7, just like your house is always there for you to live in. They also take care of security and maintenance to protect your website from potential threats.
Why Is Website Hosting Essential?
Website hosting is essential for several reasons:
- Accessibility: It ensures that your website is available 24/7, allowing potential customers to visit your site at any time.
- Performance: The type of hosting you choose can significantly impact your website’s speed and responsiveness, influencing user experience.
- Security: Hosting providers often offer security features and updates to protect your site from threats and vulnerabilities.
- Scalability: As your business grows, you can easily scale up your hosting plan to accommodate more visitors and data.
- Control: You have control over your server, which means you can install software, make customizations, and manage your website the way you want.
What is Hosting and Domain?
Hosting and domain are two fundamental components of a website’s online presence. They work together to make a website accessible on the internet.
Let’s break down what hosting and domain are and how they relate to each other.
What is Hosting?
Hosting refers to the service that provides the infrastructure and server space needed to store and serve the files, data, and content of a website on the internet. Website hosting companies, data centers, or cloud service providers maintain and operate the servers where these website files are stored.
Here are key points to understand about hosting:
- Server Space: When you create a website, you generate various files, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, videos, and databases. Hosting companies store these files on their servers, which are high-powered computers designed to be always online and connected to high-speed internet.
- Accessibility: The hosting server ensures that these files are accessible to users worldwide. When someone enters your website’s domain name in their web browser, the browser sends a request to the hosting server, which then retrieves and sends the website files to the user’s browser for display.
- Types of Hosting: There are various types of hosting, including shared hosting (multiple websites share the same server), VPS hosting (a virtualized portion of a server with dedicated resources), dedicated hosting (an entire server exclusively for your website), and cloud hosting (utilizing a network of virtual servers for scalability).
What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is the human-friendly web address that users enter in their web browsers to access a specific website. It serves as a way to locate and identify websites on the internet.
Key points about domains include:
- Unique Identifier: Each domain name is unique and corresponds to a specific IP address. The domain name system (DNS) is responsible for translating these human-friendly domain names into numerical IP addresses, which are used by the internet to locate the corresponding servers.
- Registration: To use a domain name, you must register it through a domain registrar, an accredited organization that manages the assignment and distribution of domain names. Domain registrations are typically renewed on an annual basis.
- Ownership: When you register a domain, you essentially purchase the right to use that specific domain name for a set period. You can control its settings, including where it points (the hosting server’s IP address).
How They Work Together
Website hosting and domain work together to make a website accessible. Here’s how they collaborate:
- Website Files: Your website files are hosted on a hosting server, which stores and manages these files.
- Domain Configuration: When you register a domain, you configure its DNS settings to point to the IP address of the hosting server where your website files are stored.
- User Access: When a user enters your domain name in their browser, the DNS system directs the request to the appropriate hosting server. The hosting server then retrieves the requested files and sends them to the user’s browser for display.
What is a Hosting Server?
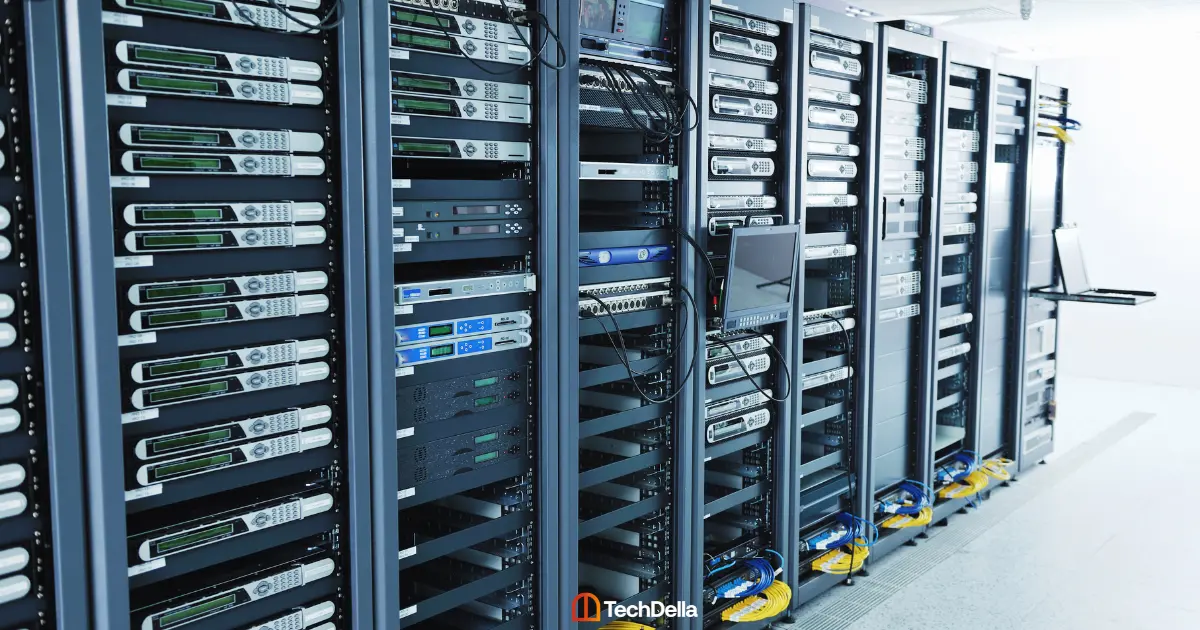

A hosting server, often simply referred to as a server, is a powerful computer or network of computers that provides the infrastructure and resources necessary to store, manage, and serve website files, data, and content to users over the internet.
Hosting servers are a critical component of website hosting services and play a central role in making websites accessible online.
Here are the key aspects and functions of a hosting server:
- Storage: Hosting servers are equipped with large amounts of storage space, typically in the form of hard drives or solid-state drives. This storage is used to store all the files that make up a website, including HTML documents, CSS stylesheets, JavaScript code, images, videos, databases, and more.
- Data Management: Hosting servers are responsible for managing the data associated with a website. This includes databases that store dynamic content, user information, and other data required for the website’s functionality.
- Accessibility: Hosting servers are designed to be connected to the internet 24/7. They have high-speed internet connections to ensure that website files and data can be retrieved and delivered quickly and reliably to users’ web browsers when they access a website.
- Processing Power: Servers are equipped with robust processors (CPUs) to handle the various tasks required to process user requests, execute scripts, and interact with databases. The server’s processing power contributes to the website’s speed and responsiveness.
- Security: Hosting servers are responsible for implementing security measures to protect the website’s files and data from unauthorized access, hacking attempts, and other security threats. This includes firewall configurations, intrusion detection systems, and software updates to address vulnerabilities.
- Redundancy: Many hosting servers are designed with redundancy in mind to minimize downtime. This means that they may have backup power supplies, duplicate hardware components, and data backups to ensure that the website remains accessible even in the event of hardware failures or other issues.
- Scalability: Hosting servers can often be scaled up or down to accommodate changing demands. In cases of high traffic or resource-intensive websites, additional server resources can be allocated to maintain optimal performance.
- Operating System and Software: Hosting servers run specialized operating systems (such as Linux or Windows Server) and software that facilitates the hosting of websites. They support web server software (e.g., Apache, Nginx), database management systems (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL), and other necessary components..
Types of Website Hosting
Web hosting comes in various forms, and the choice of hosting depends on the specific needs and requirements of a website.

Here are some common examples of website hosting:
- Shared Hosting: Shared hosting is a cost-effective option where multiple websites share the same server and its resources. It’s suitable for small websites, personal blogs, and entry-level hosting needs.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting: VPS hosting offers a virtualized portion of a physical server with dedicated resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage. It provides more control and better performance compared to shared hosting and is suitable for medium-sized websites and businesses.
- Dedicated Hosting: With dedicated hosting, you have an entire server all to yourself. This option provides maximum control, performance, and security. It’s ideal for large websites, high-traffic eCommerce platforms, and businesses with specific requirements.
- Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting uses a network of virtual servers that are interconnected. This hosting type offers scalability, redundancy, and flexibility, making it suitable for websites with varying traffic levels and resource demands.
- Managed WordPress Hosting: Specifically designed for WordPress websites, managed hosting services take care of technical aspects such as updates, security, and performance optimization. This allows website owners to focus on content and business growth.
- Reseller Hosting: Reseller hosting is a form of shared hosting where individuals or businesses purchase hosting resources and then resell them to their own clients. It’s commonly used by web designers, developers, or agencies to provide hosting services to their customers.
- eCommerce Hosting: eCommerce hosting is tailored to the specific needs of online stores. It often includes features like secure payment processing, SSL certificates, and pre-installed eCommerce platforms like Magento or WooCommerce.
- Email Hosting: Some hosting providers offer specialized email hosting services, allowing businesses to host their email accounts and communication services independently from their website hosting. This can improve email reliability and security.
- Free Hosting: Some providers offer free hosting services with limited resources. These are suitable for personal websites or small projects, but they often come with restrictions and limited support.
- Colocation Hosting: In colocation hosting, you own the physical server hardware, but you rent space in a data center facility, where you can house and maintain your server while benefiting from the data center’s infrastructure, including power, cooling, and internet connectivity.
- Green Hosting: Green hosting providers focus on using eco-friendly practices, such as renewable energy sources and energy-efficient hardware, to reduce their carbon footprint. This can be an attractive option for environmentally conscious businesses.
- Game Server Hosting: Game server hosting is designed for hosting multiplayer online games. It offers the necessary resources and infrastructure to ensure smooth gameplay and low latency for players.
- File Hosting: File hosting services are specialized for storing and sharing files, documents, and media. They often include features for sharing download links and collaborating on files.
- Video Hosting: Video hosting services are specifically designed to store and stream videos. Popular examples include YouTube and Vimeo, which offer free video hosting with extensive video management features.
- Database Hosting: Database hosting providers focus on hosting databases, making them suitable for businesses that require a database-driven website or application. These services often offer optimized database performance.
These are just a few examples of web hosting options available. When choosing a hosting solution, it’s essential to consider factors like the type of website, traffic, scalability, security, and budget to determine the most suitable hosting service for your specific needs.
In Conclusion
Website hosting provides the infrastructure and server space necessary to store, manage, and serve website files and data to users worldwide. The choice of hosting depends on various factors, including the size and complexity of the website, traffic levels, and specific requirements.
Whether you’re running a small blogging business, a thriving eCommerce store, a dynamic mobile app development business, or any other online project, there’s a website hosting solution to match your needs. From shared hosting for budget-conscious users to dedicated hosting for businesses with high demands, the hosting industry offers a diverse range of services to cater to a wide array of websites and applications.
Selecting the right website hosting solution is a critical decision that can impact your website’s performance, security, and scalability. It’s essential to assess your requirements, budget, and long-term goals when making this choice.
With the right hosting service in place, your website can thrive in the digital landscape, delivering content, services, and experiences to users worldwide, around the clock.
Need to drive traffic to your website? Book a discovery call today and we’ll help you pull in organic traffic!
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Previous Post
Next Post
Search Posts
About Us
At Techdella, we’re all about empowering businesses and startups with the tools, tips, and insights they need to thrive. From tech trends to marketing strategies, social media hacks to website tips, we break it all down in a fun, easy-to-digest way. Let’s innovate, grow, and win together!
Tags
Blogging Business Blog Niches Business Growth Business Guide Business Ideas Business Owners Business plan Cybersecurity Digital Marketing Digital Products Domain Names Early stage entrepreneurs ecommerce eCommerce Marketing Email Marketing Email marketing tools Entrepreneur’s Guide Featured Holiday Marketing Holiday promotions Influencer Marketing Marketing Marketing Campaign Marketing tools Mobile App Business Mobile Apps Monetization Tips Popular Promotions SaaS Business SEO seo for startups SEO Marketing Small Business Guide Social Media Campaign Social media marketing Software Business Startup Guide Startup teams startup tools Tech Startups VPN Website Hosting Website Monetization WordPress Hosting

























